Master Yoga at Its Birthplace with a Yoga Alliance Certified School



Train under highly experienced yoga teachers who bring years of knowledge and dedication to their teaching.

Our course combines traditional yoga practices with contemporary teaching strategies, ensuring a thorough understanding of yoga's diverse aspects.

Our school is located in Rishikesh, known for its tranquil environment that fosters deep learning and spiritual growth.

The curriculum includes Hatha, Ashtanga, meditation, and pranayama, equipping you with the knowledge to teach and inspire others.

Graduates are eligible to register as Registered Yoga Teachers (RYT) with Yoga Alliance, allowing for international recognition of their qualifications.

Immerse yourself in our 26-day residential Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh. Experience intensive 8-hour daily classes with 7 expert teachers across 15 subjects.

Earn a globally recognized Yoga Alliance certificate, empowering you to register with any yoga federation worldwide and elevate your teaching credentials.
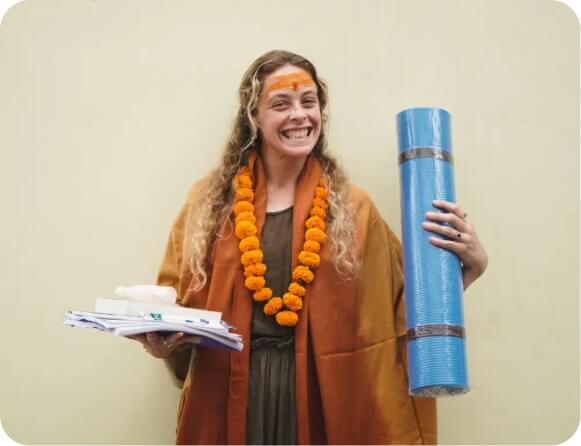

With this certification, you're qualified to teach yoga anywhere across the globe or even establish your own yoga school.
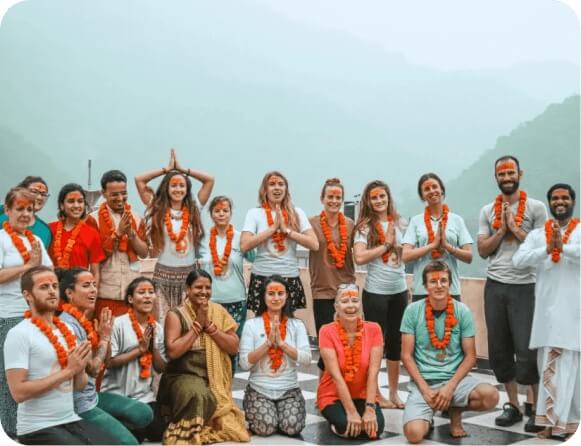

Connect with a diverse network of like-minded individuals, fostering both personal and professional growth through shared experiences and support.
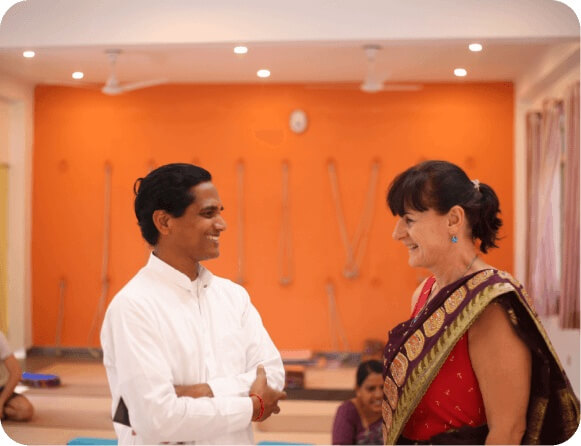

Our course uniquely emphasizes the development of soft skills through observation classes designed to enhance your communication abilities—essential for successful teaching and leadership.
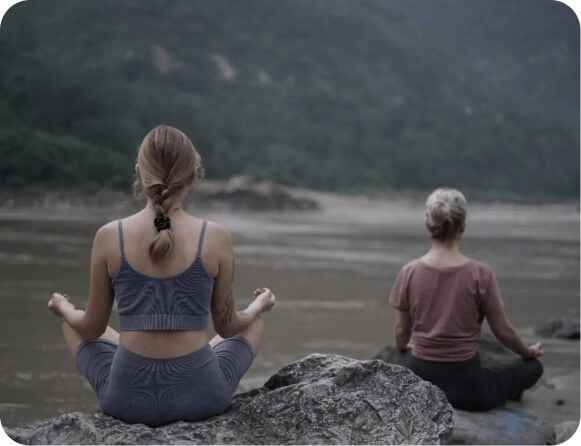

Dive into a journey of self-discovery and inner peace. This course facilitates deep explorations into mindfulness, meditation, and yoga’s spiritual aspects, enabling profound physical, mental, and spiritual transformation.
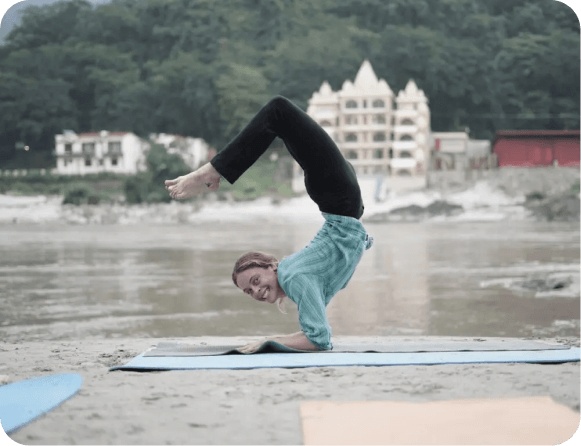

This comprehensive training not only deepens your own yoga practice but also enhances your self-awareness, setting a foundation for a fulfilling and impactful career in yoga.
Feel free to contact us. We will get back to you as soon as possible.

Certified
Masters
Premium
Accommodation
Safe
Environment
Designed to Equip You with Holistic Yoga Knowledge and Skills
05:30 AM
Wakeup
06:30 AM – 08:00 AM
Traditional Hatha Yoga &
Alignments
08:30 AM – 09:30 AM
Breakfast Time
09:30 AM – 10:30 AM
Yin Yoga, Ayurveda & Mantra Chant
09:30 AM – 10:30 AM
Anatomy & Alignment
10:45 AM – 12:15 PM
Meditation, Pranayama,
Mudra, Bandha, & Satkarma
01:00 PM – 02:00 PM
Delicious Indian lunch

02:30 PM – 03:30 PM
Yoga Pholosophy
04:00 PM – 05:00 PM
Kundalini & Tantra Yoga
05:30 PM – 07:00 PM
Ashtanga Vinyasa &
Alignments
07:00 PM – 08:00 PM
Enjoy Your Dinner
08:00 PM – 09:00 PM
Home Work & Assignments
09:00 PM
Rest/Silence Untile Breakfast

Hatha Yoga
Hatha Yoga is one of the branches of yoga, which utilizes the physical body and external aura, to reach higher levels of consciousness. It is practiced at a slower pace, in comparison to other forms of yoga. The Hatha Yoga stream consists of various controlled movements and stretching. While doing the same, the maximum focus will be on your breath. It is the best, if you have just started on your yoga journey. If you are just starting out, Hatha Yoga can bring about a balance in two different levels of energy. So, it is also a form of initiation into the holistic ambiance. Hatha Yoga helps in the preparation for more higher forms of yoga, like Ashtanga Vinyasa, which are more dynamic. Unless your body is fit enough, you cannot do such dynamic poses. Moreover, Hatha Yoga prepares the mind for greater acceptance. So, you can use Hatha Yoga as a step towards a higher journey. It is very grounding in nature as well.
Students Will Learn About Each Asana (Posture)
Each Asana Includes

Name of the Asana in English & Sanskrit

Introduction & History of Asana

Benefits

How to do this Asana dynamic way step by step?

How to do this Asana doing meditatively by following 6 steps?

Anatomical aspects of the Asana

Therapeutically approaching

Corrections

Modifications

Contraindications

Reference books

Conclusion
STANDING POSTURES

Tadasana (Mountain Pose)

Urdvahastasana – Raised Hand Pose

Tiryaki Tadasana – Swaying Palm Tree Pose

Uttkatasana – Chair Pose

Kati Chakrasana – Waist Rotating Pose

Tiryak Kati Chakrasana – Swaying Waist Rotating Pose

Meru Pristhasana – Spine and Back Pose

Uttanasana – Standing Forward Bend Pose

Malaasana – Squat or Garland Pose

Parivrita Uthita Hasta Pada Angustasana – Revolved

Uthita Hasta Pada Angustasana – Extended Hand to Big Toe Pose

Parivrita Prasarita Padotanasana – Revolved Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Prasarita Padotanasana – Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Pada Hastasana – Hand Under Foot Pose

Pada Angustasana – Big Toe Pose

Natarajasana – King Dancer Pose

Garudassana – Eagle Pose

Vrikshyasana – Tree Pose

Parivrita Konasana – Revolving Angle Pose

Konasana – Angle Pose

Parsvakonasana/ Utthita Parsvakonasana

Parivrita Trikonasana – Revolving Triangle Pose

Trikonasana – Triangle Pose/ Utthita Trikonasana

Dwikanasana – Double Angle Pose

Samakonasana – Straight Angle Pose

Druta Utkatasana – Dynamic Energy Poses

Ardhabadha Padmatanasana – Half Bound Lotus Intense Stretch Pose

Parsvatanasana – Intense Side Stretch Pose

Virbhadrasana A – Warrior Pose

Virbhadrasana B – Warrior Pose

Virbhadrasana C – Warrior Pose

Viparita Virbhadrasana – Reverse Warrior Pose (after Virbhadrasana A)

Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Parivrita Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Parivrita Badha Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Uthita Parivrita Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Ardha Chandrasana – Half Moon Pose (after Virbhadrasana C)

Dekasana – Airplane Pose (after Virbhadrasana C)
SITTING POSTURES

Sukhasana – Easy Pose

Swastikasana – Auspicious Pose

Padmasana – Lotus Pose

Sidhasana – Master/Accomplish Pose

Vajrasana – Thunderbolt Pose

Supta Vajrasana – Reclining Thunderbolt Pose

Maitriasana – Friendship Pose

Ardha Padmasana – Half Lotus Pose

Badha Padmasana – Binding Lotus Pose

Virasana – Hero Pose

Supta Virasana – Reclining Hero Pose

Eka Pada Supta Virasana – One Leg Reclining Hero Pose

Byaghrasana – Tiger Pose

Simhasana – Lion Pose

Badhakonasana/Bhadrasana – Bound Angle Pose/Butterfly Pose

Ardhabadha Konasana

Yogasana

Gorakhyasana

Guptasana

Sankatasna

Supta Badhakonasana/Bhadrasana – Reclining Bound Angle Pose/Butterfly Pose

Dandasana – Stick/Staff Pose

Uthitta Padmasana – Raised Lotus Pose

Dolasana/Lolasana/Tulasana – Scale Pose

Malasana – Garland Pose

Ardha Mastyendrasana – Half Fish Pose

Gomukhasana – Cow Face Pose

Vatayanasana – Horse Face Pose

Privrita Surya Yantrasana – Compass Pose

Poschimotanasana – Intense Back Stretching Pose

Vrisaasana – Bull Pose

Mandukasana – Frog Pose

Kurmasana – Tortoise Pose

Supta Kurmasana – Reclining Tortoise Pose

Matsyasana – Fish Pose

Parvatasana – Mountain Pose

Akarna Dhanurasana – Archer’s Pose/Bow & Arrow Pose

Paryankaasana – Couch Pose

Virasana

Trianga Mukhaika Pado Pascimottanasana – Three Limbs Forward Bend Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Pascimotanasana – Half Bind Lotus West Stretch

Janu Sirasana ABC – Head to Knee Pose

Parighasana – Gate Pose

Marichaasana ABCD – Sage Twist Pose

Navasana – Boat Pose

Bhujapidasana – Shoulder Press Pose

Garbhapindasana/Garbhasana – Embryo in Womb Pose

Upavista Konasana – Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Parivrita Upavista Konasana – Revolving Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Urdva Upavista Konasana – Upward Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Supta Konasana – Reclining Angle Pose

Supta Padongustasana ABC – Reclining Hand to Big Toe Pose

Ubhaya Padongustasana – Both Big Toe Pose

Hanumanasana & variation – Monkey Pose – side, front, backbend
BACKWARD BENDING POSES

Marjariasana – Cat Pose

Byaghrasana – Tiger Pose

Urdwamukha Swanasana – Upward Facing Dog Pose

Bhujangasana – Cobra Pose

Sarpasana – Snake Pose

Ardha Shalabhasana – Half Locust Pose

Salbhasana – Locust Pose

Naukasana – Boat Pose

Ardha Dhanurasana – Half Bow Pose

Dhanurasana – Bow Pose

Ustrasana – Camel Pose

Eka Pada Kapotasana – One Leg Pigeon Pose

Kapotasana – Pigeon Pose

Matsyasana – Fish Pose

Chandrasana – Moon Pose

Chakrasana – Wheel Pose

Urdva Dhanurasana – Upward Bow Pose

Purvattanasana – Upward Plank Pose

Setubandhasana – Bridge Pose

Uttanapadasana – Raised Legs Pose

Utthan Pristhasana – Lizard Pose

Ashva Sanchalanasana – Equestrian Pose

Uttanapadasana – Raised Legs Pose

Utthan Pristhasana – Lizard Pose

Ashva Sanchalanasana – Equestrian Pose
FORWARD BENDING POSTURES

Balasana – Child Pose

Kapotasana with Forward Bend

Hanumanasana with Forward Bend

Parsvatanasana

Astanga Namaskar – Eight Limbs Salute Pose

Adhomukha Svanasana – Downward Facing Dog Pose

Padangustasana – Big Toe Pose

Padahastasana – Hand Under Foot Pose

Prasarita Padatanasana ABCD – Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Uthitahasta Padangustasana – Extended Hand to Big Toe Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Tanasana – Half Bind Lotus Intense Stretch Pose

Badhakonasana with Forward Bend – Bound Angle Pose

Pashcimottanasana – Intense West Stretch Pose

Trianga Mukhaika Pada Pascimottanasana – Three Limbs Forward Bend Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Pascimotanasana – Half Bind Lotus Intense West Stretch Pose

Janu Sirasana ABC – Head to Knee Pose

Parivrita Janusirasana

Navasana – Boat Pose

Garbhapindasana – Embryo in Womb Pose

Urdvamukha Pashcimotanasana – Upward-Facing Intense West Stretch Pose

Halasana – Plough Pose

Karnapidasana – Knee to Ear Pose/Ear Pressure Pose

Bhunamana Asana

Kurmasana
SPINAL TWISTING POSES

Uttkata Konasana – Goddess Pose (Twist variations)

Revolving Uttanasana (Variation)

Parivita Prasarita Padotanasana – Revolved Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Parivrita Konasana – Revolving Angle Pose

Parivita Trikonasana – Revolving Triangle Pose

Move your body side to side (Dynamic)

Marichasana ABCD – Sage Twist Pose

Vakrasana – Half Spinal Twisting

Twist in Kneeling Pose

Twist in Bidalasana (Cat Pose)

Twist in Dandasana

Ardha Mastyendrasana – Half Fish Pose

Triyaka Bhujangasana – Twisting Cobra Pose

Supta Matsyendrasana – Twist in Laying Back (Variations)

Markatasana – Monkey Spinal Twisting

Meru Wakrasana – Spinal Twist with leg extend

Bhunamanasana – Spinal Twist Prostration Pose

Parivritti Janu Sirshasana – Revolved Head to Knee Pose
FIRE SERIES – ASANAS FOR ABDOMEN

Agnisaara – Agni = Fire, Saara = Flush out (Flush out Toxins)

Uthita Hasta Padongustasana D – Extend Hand to Big Toe Pose

Plank Pose – Phalakasana – Variations

Leg lifting – Laying on back – Variations

Navasana – Boat Pose

Urdva Prasarita Eka Padasana

Urdvaprasarita Padasana
BALANCING POSES

Santolanasana – Balancing Pose

Vrikshyasana – Tree Pose & variations

Natarajasana – King Dancer Pose

Eka Pada Urdwa Hastasana – One Leg Upright Hand Pose

Ardha Chandrasana – Half Moon Pose

Utthita Padmasana – Raised Lotus Pose

Dolasana – Scale Pose

Bakasana – Crow Pose

Mayurasana – Peacock Pose

Padma Mayurasana – Lotus Peacock Pose

Vasistasana – Side Plank Pose

Pincha Mayurasana – Feathered Peacock Pose (Pincha = Feather)

Visvamitrasana – Sage Visvamitra Pose
INVERSION POSES

Setubandhasana – Bridge Pose

Viparitikarani – Inverted Pose

Sarvangasana – Shoulder Stand

Padma Sarvangsana – Shoulder Stand Lotus Pose

Poorva Halasana – Preliminary Plough Pose

Druta Halasana – Dynamic Plough Pose

Ardha Padma Halasana – Half Lotus Plough Pose

Halasana – Plough Pose

Karnapidasana – Knee to Ear Pose / Ear Pressure Pose

Moordhasana – Crown Based Pose

Shirsasana & Variations – Head Stand

Vrischikasana & Variations – Scorpion Pose

Adho Mukha Vrikshasna – Hand Stand Pose & its variations
RELAXATION ASANAS

Shavasana – Corpse Pose

Advasana – Reversed Corpse Pose

Jyestikasana – Superior Pose

Makrasana – Crocodile Pose

Matsya Kridasana – Flapping Fish Pose
MEDITATION ASANAS

Sukhasana – Easy Pose

Ardha Padamasana – Half Lotus Pose

Padmasana – Lotus Pose

Sidhasana – Accomplished Pose for men

Swastikasana – Auspicious Pose
Ashtanga Vinyasa
Ashtanga Vinyasa yoga is a highly active and dynamic form of yoga. You need to develop a high level of focus and intuition, to practice the Ashtanga Vinyasa flow. You can call it more like a mind-boy extreme workout. Apart from bringing suppleness to the body, it also brings clarity to the mind. The flow yoga is a system, which generates a lot of heat in the body, as well. You can remove all the clutter from your life, you are devoted to your practice of Ashtanga Vinyasa Flow. Ashtanga Vinyasa utilizes the asanas, breath, bandhas, and your gaze. You can call it Tristhana of Ashtanga. This form of yoga came into existence in the 20th century. It is often referred to as a modern version of Indian Classical Yoga. The individual asanas being linked with flow movements, drive synchronicity. You can also practice this form of yoga, without guidance. As A practitioner, one is supposed to first master the individual asanas, and then start with the rhythmic flow.
Students will learn Ashtanga Vinyas Yoga system was reconstructed from a mysterious manuscript written on a bundle of palm leaves, the Yoga Korunta. This collection of verses on HATHA YOGA was discovered in the 1930’s by Yoga master and Sanskrit scholar Sri Tirumalai Krishnamacharya and his disciple K. Pattabhi Jois while researching Sanskrit texts at a Calcutta university library. The manuscript is dated to be between 500 and 1,500 year old.
STANDING POSTURES

Samasthiti

Surya Namaskara (A & B)

Padangushtasana

Pada hastasana

Utthita Trikonasana

Parivritta Trikonasana

Utthita Parshvakonasana

Parivritta Parshvakonasana

Prasarita Padottanasana (A, B, C & D)

Parshvottanasana
INTERMEDIATE POSTURES

Pashasana

Krounchasana

Shalabhasana A, B

Bhekasana

Dhanurasana

Parsvadhanurasana

Ustrasana

Laghu Vajrasana

Kapotasana

Supta Vajrasana

Bakasana

Bharadvajasana

Ardha Matsyendraasana

Ekapada Sirsasana A, B, C

Dwipada Sirsasana

Yoga nidrasana

Tittibhasana A, B, C

Pincha Mayurasana

Karandavasana

Mayurasana

Nakrasana

Vatayanasana

Parighasana

Gomukhasana A, B, C

Supta Urdhvapada Vajrasana A, B

Mukta Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C

Baddha Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C, D

Urdhva Dhanurasana

Paschimattanasana
FINISHING POSES

Salamba Sarvangasana

Halasana

Karnapidasana

Urdhva Padmasana

Pindasana

Matsyasana

Uttana Padasana

Shirshasana

Baddha Padmasana

Yoga Mudra

Padmasana

Uth Pluthi (Tolasana)

Shavasana
KUNDALINI YOGA
The term ‘Kundalini’ is the dormant spiritual energy that is stored in the Muladhara or the root chakra. The practice of Kundalini yoga , awakes the snake lying there in the physical body. The aroused snake rises through the chakras of the body upwards including the basal chakra. Moreover, the same activates the energy of each one of the chakras, as it passes through them. You can increase the vibrations of your body through this. The essential components are breath, movement, and the sound. A typical Kundalini session starts with mantras, as they help to calm the mind. You can seamlessly move into physical exercises after a session. The kriyas come after this stage, followed by relaxation, meditation, and affirmation. The final goal is self-awareness.
Experience a subtle shift in the energies with the practice of this Kundalini yoga form. The chanting, mantras, energy guidance, and meditation helps to release locked pain from the body. The old wounds are healed as well. Moreover, it also helps to attract more gratitude from the universe. You can gain mastery and control over your breathing patterns and can stop unhealthy habits. Connect with the divine with the help of Kundalini yoga. Additionally, you can wear white-colored clothes during the practice. It helps to ward off unwanted feelings and attract positivity. You will find the teachers wearing white clothes to protect the thoughts and life patterns. This intense yoga form can uplift the mind, body, and spirit, so you should also take up Kundalini yoga so as to benefit from the modality.


By the regular practice of Kundalini, it helps in achieving a healthy and flexible body

Pranayama and Kriyas eliminate diseases from your mind and body

Kundalini practice enhances your immunity by becoming free from several diseases

High self-awareness and more receptiveness

Purification of body decreasing toxins

Awareness of breath that enhances well-being

Good life discipline

Real spiritual awakening

Good control over energy that assists in all kinds of healing
Pranayama
Pranayama is mentioned in Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras, as the fourth limb. It is a science of breathwork. It includes controlling your breath in different ways and for varying length of time. Prana means ‘vital life force’ and Ayama means ‘expansion or extension or expanding the dimension of Prana. You can elevate the energies around you with the help of Pranayama. It is an exercise for physical as well as mental health. The main purpose of Pranayama is to connect the body and the mind. When you slow down breathing patterns, you can also increase longevity. That is the reason why some animals live longer than humans. The core reason of existence is your breathing pattern. Nadi Shodhana or Alternate Nostril Breathing is one of the most commonly taught Pranayamas. You can make it a part of your life. It involves exhalation and inhalation, through one nostril at a time. When you retain the breath between each exhalation and inhalation, it can lead to conservation of energies. Likewise, you can also practice Anuloma Viloma. It is another variety that can give you the calmness you are looking for, in your life.
Pranayama is the integral part of Yogic Practices also mention in the eight limbs of Patanjali Yoga sutras. Pranayama specifically focus on the increase the efficiency and balancing the breath of an individual. Prana is vital energy of the body and yama refers to the expansion and growth. There are many physiological and psychological benefits by doing pranayama practices daily.
Introduction of Pranayama

Meaning of Pranayama

Definition

Breathing experiment

Conclusion
Advance Kapalbhati Pranayama (Frontal Brain Cleaning Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Kapalabhati Pranayama

Preparation of Kapalabhati for students – Technique One

How to do Kapalabhati Pranayama?
Advance Sheetali Pranayama (Cooling Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Sheetali Pranayama

Preparation of Sheetali for students
Advance Sheetkari Pranayam (Hishing Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Sheetkari Pranayama

Preparation of Sheetkari for students
Advance Bhastrika Pranayam (Bellows Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhastrika Pranayama

Preparation of Bhastrika for students

Technique One

How to do Bhastrika Pranayama?
Advance Bhramri Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhramri Pranayama

Preparation of Bhramri for students

Technique One

How to do Bhramri Pranayama?
Advance Ujjayi (Psychic Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Ujjayi Pranayama

Preparation of Ujjayi for students

Technique One

How to do Ujjayi Pranayama?
Advance Nadishodhana Pranayama (Psychic Network / Chanel Purification)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Duration of practice

Demonstration of Nadishodhana Pranayama

Preparation of Nadishodhana for students

Technique One

How to do Nadishodhana Pranayama?
Advance Kapalbhati Pranayama 2 (Frontal Brain Cleaning Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Kapalabhati Pranayama Two

Preparation of Kapalabhati for students

Technique Two

How to do Kapalabhati Pranayama?
Advance Sheetali Pranayama 2 (Cooling Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Sheetali Pranayama Two

Preparation of Sheetali for students

Technique Two

How to do Sheetali Pranayama?
Advance Sheetkari Pranayam 2 (Hishing Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Sheetkari Pranayama Two

Preparation of Sheetkari for students

Technique Two

How to do Sheetkari Pranayama?
Advance Bhastrika Pranayam (Bellows Breath) 2 & 3

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhastrika Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Bhastrika for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Bhastrika Pranayama?
Advance Bhramri Pranayama 2 & 3 (Humming Bee Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhramri Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Bhramri for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Bhramri Pranayama?
Advance Ujjayi (Psychic Breath) 2 & 3

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Ujjayi Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Ujjayi for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Ujjayi Pranayama?
Advance Nadishodhana Pranayama 2 & 3 (Psychic Network / Chanel Purification)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Nadishodhana Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Nadishodhana for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Nadishodhana Pranayama?
Satkarma
The Shatkarmas are also called Shatkriyas. It is a set of body purification techniques, with the help of which, you can cleanse your system internally. In order to move ahead in your yogic journey, you need to have a strong body, as it serves as the foundation for yoga sadhana. Shatkarmas consists of six cleansing techniques, like Basti, Nauli, Dhauti, Trataka, Neti, and Kapalbhati. Each of these kriyas target specific organs in the alimentary canal. Apart from just strengthening the body, it also leads to the balance of the Tridoshas. It also helps in the flow of Prana through the Nadis. . Kapalbhati is not only a kriya, but it is also a Pranayama. So, you get to indulge in two practices, rolled into one. It is a forceful breathing practice, that can aid in alleviating stress from your brain. You can also practice Neti, very easily. However, a guide will initiate the process, for you to feel comfortable later on.
Six Steps of Cleansing – Subject focus on Jala Neti & Sutra Neti

Introduction to Six Types of Satkarma

Meaning of Satkarma

Contradictions

Benefits
Introduction to the Practical Jala Neti

Contradictions

Benefits

Preparation of Jala Neti

Demonstration of Jala Neti by Teacher

Technique Practice with students
Introduction to the Practical Sutraneti

Contradictions

Benefits

Preparation

Demonstration of Sutraneti by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students
Introduction to the Practical Kunjala Kriya

Contradictions of Kunjala Kriya

Benefits of Kunjala Kriya

Preparation of Kunjala Kriya

Demonstration of Kunjala Kriya by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Kunjala Kriya
Introduction to the Practical Vat Karma

Contradictions of Vat Karma

Benefits of Vat Karma

Preparation of Vat Karma

Demonstration of Vata Karma by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Vat Karma
Introduction to the Practical Nauli Kriya

Contradictions of Nauli Kriya

Benefits of Nauli Kriya

Preparation of Nauli Kriya

Demonstration of Nauli Kriya by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Nauli Kriya
Introduction to the Practical Agneesara

Technique Practice with Students for Agneesara

Demonstration of Agneesara by Teacher

Preparation of Agneesara

Benefits of Agneesara

Contradictions of Agneesara
With presence of teacher
With presence of teacher, students will prepare the class to practice Jala Neti, Sutra Neti, Kunjala kriya, Vat Karma, Nauli kriya and Agneesara them self. Techer will observe the class.
Bandhas

Jalandhara Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Udiyana Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Mula Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Maha Bandha Advance

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Mudra – Gesture
A mudra is a gesture or seal in yoga. You may come across mudras in dance forms as well, however, they are much different. When you practice mudras, you can channelize Prana through the body. There are various kinds of mudras, like Hasta mudras, Kaya mudras, and Chitta Mudras. Hasta mudras are the most important in Yoga practice. According to the Science, Ayurveda, there are five elements or Mahabhutas. Fire, earth, air, water, and ether. Each finger represents one maha bhuta. You can manipulate each element for the betterment of your body and health, and increase or decrease the flow of prana to specific body parts. One of the most commonly used mudras, is Gyan mudra. You can practice it while performing the asanas. It helps in obtaining knowledge and greater wisdom from the universal body. You can practice mudras anywhere, while sitting in your home or workplace, so that is an added benefit of mudras. Get the maximum benefits today.

Jnana Mudra (Psychic Gesture of Knowledge)

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Chin Mudra (Psychic Gesture of Consciousness)

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Bhairava Mudra – Shiva Mudra

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Hridaya Mudra – Heart Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Yoni Mudra – Womb Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Shambhavi Mudra – Eyebrow Center Gazing Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Kaaki Mudra – Crow’s Beak Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Ashwini Mudra – Horse Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Meditation
Meditation is a set of practices that encourage higher states of consciousness, awareness, and focused attention. Moreover, it is not just a part of yoga. Every culture practice meditation. People practice meditation for spiritual as well as religious reasons. In the Western World, meditation has been shown to help people cope with stress, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. It is all about training your awareness. You learn to observe your thoughts and patterns, without any judgement. Moreover, everyone can meditate. There is no age boundation or health boundation. So, it is a universal practice, that goes beyond the physical body. . If you are just starting out and find it extremely difficult to practice meditation, you can also use props, like meditation seats, malas, and singing bowls. It will alleviate the strength of your practice. Meditation can cure the most incurable diseases, as per research. Always practice in a clean and calm place. Lots of sunlight is also important.
Introduction of Meditation/ Meaning and Things

Mantra Chanting with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

Apa Meditation with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

Sixty One Energy Points Discussion

OM Meditation with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

The Practice of Osho Dynamic Meditation

Music Meditation Practice

Dancing Meditation Practice

Walking Meditation Practice

Introduction of Tratak Meditation/Stages/Benefits

The Practice of Dot Meditation

The Practice of Yantra Meditation
Yogic Relaxation Techniques
The answer to life’s stress and tension is yoga. It has been widely researched, that yoga can change your life, by reducing stress and anxiety. No matter, where you are, at work or at home, yoga can help you. If you are new to yoga, you can start your yoga journey with mindfulness. Your breath is the single-most thing, that can alleviate the mind, body and soul. Moreover, mindfulness is the main modality, that can alleviate your symptoms. When you move into the postures, you should ensure to think about your own self-respect and self-care. It is the curiosity towards yourself, that can help you relax. Some of the easy poses, that you must practice today are Sukhasana, Uttanasana, and Tadasana, to name a few. These are very easy for one and all. You can practice the asanas, after a few hours of having your food. When the stomach is full, your body’s energies are aligned toward the stomach. So, you will not be able to utilize them to their full strength. Apart from poses, you can also utilize breathing techniques. Meditation and relaxation are inter-linked. You have to utilize breathing to guide the poses, and it should not be the other way round. That is when, you can gain the true benefits of yoga. The best part of yoga relaxation is that, you can practice it anywhere and everywhere. So, it is universal in nature and beyond boundaries. Start relaxing now, with myriad yoga practices. It is one of the ancient sceiences that has cleared clutter from the minds of millions.

Synopsis of Featured Teachings

Point-to-Point Movement and then Stillness

Point-to-Point Tension and Relaxation

Entire-Body Tension and Relaxation

Point-to-Point Relaxation

Selective Tension and Relaxation of Body Parts

More Detailed Point-to-Point Relaxation with Visualization of Pure White Divine Light at the Cardiac Center

Detailed Point-to-Point Relaxation with Spinal Breathing and “So-Ham”
Alignment, Correction & Adjustment
Alignment and adjustment are fundamental concepts in the practice of Yoga, both for practitioners and instructors. Here’s a breakdown of each:
What is alignment in Yoga?
Alignment refers to the precise positioning of the body in Yoga poses (Asanas) to achieve optimal physical and energetic benefits while minimizing the risk of injury. It involves the correct placement of various body parts, such as the feet, legs, pelvis, spine, arms, and head, in relation to one another and to the ground. Proper alignment ensures that the body is in a balanced and stable position, allowing for the efficient flow of energy (Prana) throughout the body. It also helps to create space within the joints, improve posture, enhance flexibility, and build strength. Alignment principles may vary depending on the specific Yoga style or tradition but generally emphasize alignment with the natural curves of the spine and engagement of relevant muscle groups.

What is Adjustment in Yoga?
Adjustment, also known as hands-on adjustment or assists, involves the gentle physical manipulation of a student’s body by the instructor to help them refine their alignment, deepen their stretch, or experience a pose more fully. Adjustments can provide valuable feedback and support to students, helping them overcome physical limitations, release tension, and access deeper levels of awareness in their practice. Adjustments are typically performed with sensitivity and mindfulness, respecting the individual’s body and boundaries. They may include subtle corrections to alignment, gentle pressure to encourage relaxation or engagement, or supportive touch to guide the student into a safer or more effective expression of a pose.

Roll of alignment and adjustment in Yoga concept

Physical Alignment in Yoga

The Role of Adjustment

Benefits Beyond the Physical

Alignment and Adjustment in Spiritual Practice

The Role of Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga: A Comprehensive Overview

Understanding Alignment in Yoga
Spine
Joints
Muscles
Physical Adjustments
Verbal Adjustments

Components of Alignment

Challenges and Considerations in Adjustment

Integrating Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga Practice

Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga Asanas for Students Homework
Teaching Methodology
TEACHING METHODOLOGY

Teaching is an art and it can be developed through practice and knowledge.

Teach with sincerity and compassion for yourself first and then your students will benefit as well.

Teach from the heart, never from the mind.

Respect that divine energy has honored you to be a teacher to help people.

Changing peoples’ lives into positivity by teaching them yoga and meditation; as a teacher, your inner journey and happiness will grow.

Respect the students, be friendly and professional but at the same time strong inside not to entertain any negativity while teaching yoga.

Surrender to life and divine energy; you will feel guided by the unknown force.

Enjoy teaching mindfully with joy and happiness.

Be present, aware, and energetic all the time during or after the class.

Be regular for your own self-practice of yoga and meditation; you owe it to yourself and your students.

Be aware and sensitive to students’ poses, alignment, breathing pattern, group energy, and allow the teaching and response to happen accordingly and spontaneously.

Pay equal attention to the students but focus more attention on beginners until they catch up with the regular class.

Welcome the students – greeting the students makes them comfortable and feel welcomed.

Start the class on time and end on time. This honors the student since most students have limited time and have sacrificed to get to the class.

Always ask if the students have any physical problems and injuries.

Start the class with some chanting, prayer, or a short meditation.

The voice of the teacher should be audible to everyone and the volume should be according to the group.

Give clear instructions.

Make adjustments verbally and physically.

Appreciate and motivate the students during the class.

Move around the class effectively to see all the students and to check their alignment.
Yoga Philosophy
Along with the practical applications of yoga, you need to fall back at times, on the foundation of yoga. That is what Yoga Philosophy is all about. The main philosophy of yoga states that the minds, body, and soul are all one. You need to know about the philosophical ideas, to be able to utilize the various practices under the umbrella of yoga. In yoga, you cannot choose one or leave out another aspect. The entire practice has to be carried out in totality. Spiritual ignorance can only create suffering, and mothing more than that. So, you need to amass the wealth of knowledge that philosophy of yoga offers. You can call it the blue print of your yogic practice. It enlists what all you should follow, and what you should not. The main principle of yoga is that the mind, body and soul is one. You cannot separate one from the other. It also allows the concept of God. It is amongst the six orthodox schools.


Yoga Sutra – discipline, types of thoughts, God

7 Chakras – Muladhara, Swadhisthana, Manipur, Anahata, Visudha, Anjya, Sahasrara

Three types of gunas – Satva, Rajas & Tamas

Three types of body – Sthula, Sukhma & Karana

Types of Yoga (Hatha, Karma, Bhakti, Astanga)

What is yoga? Introduction of Yoga

What is philosophy?

What are the obstacles to yoga?

What are the causes of pain?

What are the eight limbs of Yoga?

Exercises

Exam
Ayurveda
Ayurveda is one of the ancient holistic sciences with the power to heal. It goes back to the pre-Vedic times. You can better describe it, as the ‘science of life’. It is the sister science of Yoga. It is the immense knowledge about the beings and their healing. And, you are practically applying that knowledge in the realm of yoga. According to Ayurveda, each person is governed by the Mahabhutas, Gunas, and Doshas. The five elements also assume a lot of significance, in the Pancha Mahabhuta theory. The human beings as per Ayurveda, are believed to comprise of the doshas – Vata, Pitta and Kapha. Although, you will not find them in perfect balance. Through the Avenue, you can strive for balance among these doshas. According to Ayurveda, if you ingest food according to the doshas, and your Gunas, you can become accomplished in no time. It is not just the accomplishment of physical health, but that of your mental and spiritual life. Yoga and Ayurveda are intertwined with one another. In Ayurvedic treatment, herbs, and natural substances are used in conjunction with one another. The treatments mainly rely on medicated oils, blood purification techniques, and enemas. You can make it a part of your life, through the education at Hari Om Yoga Vidya School.
Body Type as per Ayurveda

Vata – Air

Pitta – Fire

Kapha – Water
Introduction & History of Ayurveda

To Know About One’s Physical Qualities

How Yoga & Ayurveda are Connected

Diet of Ayurveda as per Physical Qualities

Some Ayurvedic Treatments

Pancha Karma – Five Different Ayurvedic Methods

Sapta Dhatu – Seven Metals of the Body & How to Achieve Balance

Elementary Disorders & Balancing Through Yoga & Ayurveda

Prana Cure through Ayurveda & Yoga

Diagnostic Sessions for Identifying Disorders

Description of Ayurvedic Herbs & Medicines According to Physical Qualities
Mantra Chanting
Mantras are group of syllables, or complete words, or phrases. Most religious and spiritual practitioners, believe them to have originated from Sanskrit. Om is the believed to be the first sound that originated on earth, and has divine connotations. It produces higher vibrations in the body and mind. Mantras also serve an important role in Tantra. You can also term it as a mind vibration that helps to focus the thoughts and feelings, and the highest intention. With time, the mantras and their vibrations sink deeper into the consciousness. You can practice mantra recitation to make your energies vibrate at a higher level. Om is one of the mantras sounds that assumes a lot of significance. It releases subtle energies, that can aid your meditation and yoga practice. You can chant mantras at any time, and place. But they have the maximum significance, when you chant them at the Brahma Muhurta. You will feel the vibrations emanating from the mantras, as you make them a part of your life.

What is Mantra?
The word “mantra” is derived from two words. The first word is “Manas” or “mind,” which relates to the “man” syllable means “To think”, the second word is a suffix “Tra” which means instruments, tools, protect, or free from. Therefore, the word Mantra in its most literal sense means “to free from the mind Mantra is a tool used by the Mind to be free from all kinds of distractions of the Mind field.
Benefits of Mantra Chanting

Hatha Yoga Mantra: Yogena Schitasya Padena Vacham

Health Mantra: Trayambakm Yajamahe

Gayatri Mantra: Om Bhur Bhubah Swaha

Ganesh Mantra: Om Vakratunda mahaakaaya

Morning Mantra: Karagre Vasate Laxmi

Guru Mantra: Akhanda Mandalakaram Guru Brahma Guru Visnu

Aum Mantra: Aum…Aum…Aum

Shanti Mantra: Om Sarve Bhavantu Sukhinah Om Saha Na bhavatu, Saha Nau Bhunaktu Om Asato Maa Sad-Gamaya, Tamaso Maa Om Purna madah Purna midam

Astanga Vinyas Mantra: Vande Gurunam Charanara Vinde Avahu Purusa Karam, shankh

Astanga Vinyas Closing Mantra: Swasti prajaabhyah paripala

Purna Mantra: Om Purna madah Purna midam
Bhajan or Spiritual Songs
A Bhajan is basically a devotional song, that you sing to glorify any particular deity or the lord in general. It is usually the ancient scriptures, from where it originates. You can sing it straightforward, or recite it like a mantra, or add some melody. Bhajan is related to Bhakti. You will learn of different styles of Bhakti songs from different parts of India. You may hear them coming from various Hindi complicated dialects, and some using various day-to-day occurrence in in simple words and forms. You will be able to get rid of mental issues, once you make such devotional hymns a part of your practice. . This kind of devotional singing is very popular at Indian pujas and rituals. Slowly the wet is also opening up to its possibilities, as it tends to calm the mind. It is a spiritual practice of sorts, where everyone participates in one go. You can also start doing this practice alone, from home.


Shiva Shiva Shambhu, Shiva Shiva Shambhu, Mahadeva Shambhu, Mahadeva Shambhu, Shiva Shiva Shambhu.

Govinda Govinda Govinda Bhaja Gopala, Gopala Gopala Gopala Bhaja Gopala.

Govinda Bol Hari Gopal Bol, Radha Ramana Hari Govinda Bol.

Hare Krishna Hare Krishna, Krishna Krishna Hare Hare, Hare Rama Hare Rama, Rama Rama Hare Hare.

Sita Ram Sita Ram, Sita Ram Jai Sita Ram, Radhe Shyam Radhe Shyam, Radhe Shyam Jai Radhe Shyam.

Raghupati Raghava Rajaram, Patita Pavana Sitaram, Ishwar Allah Tero Nam, Sab Ko Sanmati De Bhagavan.

Natavara Nagara Nanda Bhajore Mana Govinda, Natavara Nagara Nanda … Karo Nama Roj Prema se, Mana Ko Dho-Nitya Niyama se, Nirmala Mana Prabhu Ko Pasanda Hei, Mat Karo Mano Ko Ganda, Bhajore Mana Govinda.

Jai Jai Radha Ramana Hari Bol, Jai Jai Radha Ramana Hari Bol.
Hatha Yoga
Hatha Yoga is one of the branches of yoga, which utilizes the physical body and external aura, to reach higher levels of consciousness. It is practiced at a slower pace, in comparison to other forms of yoga. The Hatha Yoga stream consists of various controlled movements and stretching. While doing the same, the maximum focus will be on your breath. It is the best, if you have just started on your yoga journey. If you are just starting out, Hatha Yoga can bring about a balance in two different levels of energy. So, it is also a form of initiation into the holistic ambiance. Hatha Yoga helps in the preparation for more higher forms of yoga, like Ashtanga Vinyasa, which are more dynamic. Unless your body is fit enough, you cannot do such dynamic poses. Moreover, Hatha Yoga prepares the mind for greater acceptance. So, you can use Hatha Yoga as a step towards a higher journey. It is very grounding in nature as well.
Students Will Learn About Each Asana (Posture)
Each Asana Includes

Name of the Asana in English & Sanskrit

Introduction & History of Asana

Benefits

How to do this Asana dynamic way step by step?

How to do this Asana doing meditatively by following 6 steps?

Anatomical aspects of the Asana

Therapeutically approaching

Corrections

Modifications

Contraindications

Reference books

Conclusion
STANDING POSTURES

Tadasana (Mountain Pose)

Urdvahastasana – Raised Hand Pose

Tiryaki Tadasana - Swaying Palm Tree Pose

Uttkatasana – Chair Pose

Kati Chakrasana - Waist Rotating Pose

Tiryak Kati Chakrasana - Swaying Waist Rotating Pose

Meru Pristhasana - Spine and Back Pose

Uttanasana – Standing Forward Bend Pose

Malaasana – Squat or Garland Pose

Parivrita Uthita Hasta Pada Angustasana – Revolved

Uthita Hasta Pada Angustasana – Extended Hand to Big Toe Pose

Parivrita Prasarita Padotanasana – Revolved Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Prasarita Padotanasana – Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Pada Hastasana – Hand Under Foot Pose

Pada Angustasana – Big Toe Pose

Natarajasana – King Dancer Pose

Garudassana – Eagle Pose

Vrikshyasana – Tree Pose

Parivrita Konasana – Revolving Angle Pose

Konasana – Angle Pose

Parsvakonasana/ Utthita Parsvakonasana

Parivrita Trikonasana – Revolving Triangle Pose

Trikonasana – Triangle Pose/ Utthita Trikonasana

Dwikanasana - Double Angle Pose

Samakonasana – Straight Angle Pose

Druta Utkatasana - Dynamic Energy Poses

Ardhabadha Padmatanasana – Half Bound Lotus Intense Stretch Pose

Parsvatanasana – Intense Side Stretch Pose

Virbhadrasana A – Warrior Pose

Virbhadrasana B – Warrior Pose

Virbhadrasana C – Warrior Pose

Viparita Virbhadrasana – Reverse Warrior Pose (after Virbhadrasana A)

Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Parivrita Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Parivrita Badha Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Uthita Parivrita Anjaneyasana – Low Lunge Pose (after Virbhadrasana B)

Ardha Chandrasana – Half Moon Pose (after Virbhadrasana C)

Dekasana – Airplane Pose (after Virbhadrasana C)
SITTING POSTURES

Sukhasana – Easy Pose

Swastikasana – Auspicious Pose

Padmasana – Lotus Pose

Sidhasana – Master/Accomplish Pose

Vajrasana – Thunderbolt Pose

Supta Vajrasana – Reclining Thunderbolt Pose

Maitriasana – Friendship Pose

Ardha Padmasana – Half Lotus Pose

Badha Padmasana – Binding Lotus Pose

Virasana – Hero Pose

Supta Virasana – Reclining Hero Pose

Eka Pada Supta Virasana – One Leg Reclining Hero Pose

Byaghrasana – Tiger Pose

Simhasana – Lion Pose

Badhakonasana/Bhadrasana – Bound Angle Pose/Butterfly Pose

Ardhabadha Konasana

Yogasana

Gorakhyasana

Guptasana

Sankatasna

Supta Badhakonasana/Bhadrasana – Reclining Bound Angle Pose/Butterfly Pose

Dandasana – Stick/Staff Pose

Uthitta Padmasana – Raised Lotus Pose

Dolasana/Lolasana/Tulasana – Scale Pose

Malasana – Garland Pose

Ardha Mastyendrasana – Half Fish Pose

Gomukhasana – Cow Face Pose

Vatayanasana – Horse Face Pose

Privrita Surya Yantrasana – Compass Pose

Poschimotanasana – Intense Back Stretching Pose

Vrisaasana – Bull Pose

Mandukasana – Frog Pose

Kurmasana – Tortoise Pose

Supta Kurmasana – Reclining Tortoise Pose

Matsyasana – Fish Pose

Parvatasana – Mountain Pose

Akarna Dhanurasana – Archer’s Pose/Bow & Arrow Pose

Paryankaasana – Couch Pose

Virasana

Trianga Mukhaika Pado Pascimottanasana – Three Limbs Forward Bend Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Pascimotanasana – Half Bind Lotus West Stretch

Janu Sirasana ABC – Head to Knee Pose

Parighasana – Gate Pose

Marichaasana ABCD – Sage Twist Pose

Navasana – Boat Pose

Bhujapidasana – Shoulder Press Pose

Garbhapindasana/Garbhasana – Embryo in Womb Pose

Upavista Konasana – Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Parivrita Upavista Konasana – Revolving Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Urdva Upavista Konasana – Upward Wide Angle Seated Forward Bend Pose

Supta Konasana – Reclining Angle Pose

Supta Padongustasana ABC – Reclining Hand to Big Toe Pose

Ubhaya Padongustasana – Both Big Toe Pose

Hanumanasana & variation – Monkey Pose – side, front, backbend
BACKWARD BENDING POSES

Marjariasana – Cat Pose

Byaghrasana – Tiger Pose

Urdwamukha Swanasana – Upward Facing Dog Pose

Bhujangasana – Cobra Pose

Sarpasana – Snake Pose

Ardha Shalabhasana – Half Locust Pose

Salbhasana – Locust Pose

Naukasana – Boat Pose

Ardha Dhanurasana – Half Bow Pose

Dhanurasana – Bow Pose

Ustrasana – Camel Pose

Eka Pada Kapotasana – One Leg Pigeon Pose

Kapotasana – Pigeon Pose

Matsyasana – Fish Pose

Chandrasana – Moon Pose

Chakrasana – Wheel Pose

Urdva Dhanurasana – Upward Bow Pose

Purvattanasana – Upward Plank Pose

Setubandhasana – Bridge Pose

Uttanapadasana – Raised Legs Pose

Utthan Pristhasana – Lizard Pose

Ashva Sanchalanasana – Equestrian Pose

Uttanapadasana – Raised Legs Pose

Utthan Pristhasana – Lizard Pose

Ashva Sanchalanasana – Equestrian Pose
FORWARD BENDING POSTURES

Balasana – Child Pose

Kapotasana with Forward Bend

Hanumanasana with Forward Bend

Parsvatanasana

Astanga Namaskar – Eight Limbs Salute Pose

Adhomukha Svanasana – Downward Facing Dog Pose

Padangustasana – Big Toe Pose

Padahastasana – Hand Under Foot Pose

Prasarita Padatanasana ABCD – Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Uthitahasta Padangustasana – Extended Hand to Big Toe Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Tanasana – Half Bind Lotus Intense Stretch Pose

Badhakonasana with Forward Bend – Bound Angle Pose

Pashcimottanasana – Intense West Stretch Pose

Trianga Mukhaika Pada Pascimottanasana – Three Limbs Forward Bend Pose

Ardha Badha Padma Pascimotanasana – Half Bind Lotus Intense West Stretch Pose

Janu Sirasana ABC – Head to Knee Pose

Parivrita Janusirasana

Navasana – Boat Pose

Garbhapindasana – Embryo in Womb Pose

Urdvamukha Pashcimotanasana – Upward-Facing Intense West Stretch Pose

Halasana – Plough Pose

Karnapidasana – Knee to Ear Pose/Ear Pressure Pose

Bhunamana Asana

Kurmasana
SPINAL TWISTING POSES

Uttkata Konasana – Goddess Pose (Twist variations)

Revolving Uttanasana (Variation)

Parivita Prasarita Padotanasana – Revolved Wide Legs Forward Bend Pose

Parivrita Konasana – Revolving Angle Pose

Parivita Trikonasana – Revolving Triangle Pose

Move your body side to side (Dynamic)

Marichasana ABCD – Sage Twist Pose

Vakrasana – Half Spinal Twisting

Twist in Kneeling Pose

Twist in Bidalasana (Cat Pose)

Twist in Dandasana

Ardha Mastyendrasana – Half Fish Pose

Triyaka Bhujangasana – Twisting Cobra Pose

Supta Matsyendrasana – Twist in Laying Back (Variations)

Markatasana – Monkey Spinal Twisting

Meru Wakrasana – Spinal Twist with leg extend

Bhunamanasana – Spinal Twist Prostration Pose

Parivritti Janu Sirshasana – Revolved Head to Knee Pose
FIRE SERIES - ASANAS FOR ABDOMEN

Agnisaara – Agni = Fire, Saara = Flush out (Flush out Toxins)

Uthita Hasta Padongustasana D – Extend Hand to Big Toe Pose

Plank Pose – Phalakasana – Variations

Leg lifting – Laying on back – Variations

Navasana – Boat Pose

Urdva Prasarita Eka Padasana

Urdvaprasarita Padasana
BALANCING POSES

Santolanasana – Balancing Pose

Vrikshyasana – Tree Pose & variations

Natarajasana – King Dancer Pose

Eka Pada Urdwa Hastasana – One Leg Upright Hand Pose

Ardha Chandrasana – Half Moon Pose

Utthita Padmasana – Raised Lotus Pose

Dolasana – Scale Pose

Bakasana – Crow Pose

Mayurasana – Peacock Pose

Padma Mayurasana – Lotus Peacock Pose

Vasistasana – Side Plank Pose

Pincha Mayurasana – Feathered Peacock Pose (Pincha = Feather)

Visvamitrasana – Sage Visvamitra Pose
INVERSION POSES

Setubandhasana – Bridge Pose

Viparitikarani – Inverted Pose

Sarvangasana – Shoulder Stand

Padma Sarvangsana – Shoulder Stand Lotus Pose

Poorva Halasana – Preliminary Plough Pose

Druta Halasana – Dynamic Plough Pose

Ardha Padma Halasana – Half Lotus Plough Pose

Halasana – Plough Pose

Karnapidasana – Knee to Ear Pose / Ear Pressure Pose

Moordhasana – Crown Based Pose

Shirsasana & Variations – Head Stand

Vrischikasana & Variations – Scorpion Pose

Adho Mukha Vrikshasna – Hand Stand Pose & its variations
RELAXATION ASANAS

Shavasana – Corpse Pose

Advasana – Reversed Corpse Pose

Jyestikasana – Superior Pose

Makrasana – Crocodile Pose

Matsya Kridasana – Flapping Fish Pose
MEDITATION ASANAS

Sukhasana – Easy Pose

Ardha Padamasana – Half Lotus Pose

Padmasana – Lotus Pose

Sidhasana – Accomplished Pose for men

Swastikasana – Auspicious Pose
Ashtanga Vinyasa
Ashtanga Vinyasa yoga is a highly active and dynamic form of yoga. You need to develop a high level of focus and intuition, to practice the Ashtanga Vinyasa flow. You can call it more like a mind-boy extreme workout. Apart from bringing suppleness to the body, it also brings clarity to the mind. The flow yoga is a system, which generates a lot of heat in the body, as well. You can remove all the clutter from your life, you are devoted to your practice of Ashtanga Vinyasa Flow. Ashtanga Vinyasa utilizes the asanas, breath, bandhas, and your gaze. You can call it Tristhana of Ashtanga. This form of yoga came into existence in the 20th century. It is often referred to as a modern version of Indian Classical Yoga. The individual asanas being linked with flow movements, drive synchronicity. You can also practice this form of yoga, without guidance. As A practitioner, one is supposed to first master the individual asanas, and then start with the rhythmic flow.
Students will learn Ashtanga Vinyas Yoga system was reconstructed from a mysterious manuscript written on a bundle of palm leaves, the Yoga Korunta. This collection of verses on HATHA YOGA was discovered in the 1930’s by Yoga master and Sanskrit scholar Sri Tirumalai Krishnamacharya and his disciple K. Pattabhi Jois while researching Sanskrit texts at a Calcutta university library. The manuscript is dated to be between 500 and 1,500 year old.
STANDING POSTURES

Samasthiti

Surya Namaskara (A & B)

Padangushtasana

Pada hastasana

Utthita Trikonasana

Parivritta Trikonasana

Utthita Parshvakonasana

Parivritta Parshvakonasana

Prasarita Padottanasana (A, B, C & D)

Parshvottanasana
INTERMEDIATE POSTURES

Pashasana

Krounchasana

Shalabhasana A, B

Bhekasana

Dhanurasana

Parsvadhanurasana

Ustrasana

Laghu Vajrasana

Kapotasana

Supta Vajrasana

Bakasana

Bharadvajasana

Ardha Matsyendraasana

Ekapada Sirsasana A, B, C

Dwipada Sirsasana

Yoga nidrasana

Tittibhasana A, B, C

Pincha Mayurasana

Karandavasana

Mayurasana

Nakrasana

Vatayanasana

Parighasana

Gomukhasana A, B, C

Supta Urdhvapada Vajrasana A, B

Mukta Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C

Baddha Hasta Sirsasana A, B, C, D

Urdhva Dhanurasana

Paschimattanasana
FINISHING POSES

Salamba Sarvangasana

Halasana

Karnapidasana

Urdhva Padmasana

Pindasana

Matsyasana

Uttana Padasana

Shirshasana

Baddha Padmasana

Yoga Mudra

Padmasana

Uth Pluthi (Tolasana)

Shavasana
KUNDALINI YOGA
The term ‘Kundalini’ is the dormant spiritual energy that is stored in the Muladhara or the root chakra. The practice of Kundalini yoga , awakes the snake lying there in the physical body. The aroused snake rises through the chakras of the body upwards including the basal chakra. Moreover, the same activates the energy of each one of the chakras, as it passes through them. You can increase the vibrations of your body through this. The essential components are breath, movement, and the sound. A typical Kundalini session starts with mantras, as they help to calm the mind. You can seamlessly move into physical exercises after a session. The kriyas come after this stage, followed by relaxation, meditation, and affirmation. The final goal is self-awareness.
Experience a subtle shift in the energies with the practice of this Kundalini yoga form. The chanting, mantras, energy guidance, and meditation helps to release locked pain from the body. The old wounds are healed as well. Moreover, it also helps to attract more gratitude from the universe. You can gain mastery and control over your breathing patterns and can stop unhealthy habits. Connect with the divine with the help of Kundalini yoga. Additionally, you can wear white-colored clothes during the practice. It helps to ward off unwanted feelings and attract positivity. You will find the teachers wearing white clothes to protect the thoughts and life patterns. This intense yoga form can uplift the mind, body, and spirit, so you should also take up Kundalini yoga so as to benefit from the modality.


By the regular practice of Kundalini, it helps in achieving a healthy and flexible body

Pranayama and Kriyas eliminate diseases from your mind and body

Kundalini practice enhances your immunity by becoming free from several diseases

High self-awareness and more receptiveness

Purification of body decreasing toxins

Awareness of breath that enhances well-being

Good life discipline

Real spiritual awakening

Good control over energy that assists in all kinds of healing
Pranayama
Pranayama is mentioned in Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras, as the fourth limb. It is a science of breathwork. It includes controlling your breath in different ways and for varying length of time. Prana means ‘vital life force’ and Ayama means ‘expansion or extension or expanding the dimension of Prana. You can elevate the energies around you with the help of Pranayama. It is an exercise for physical as well as mental health. The main purpose of Pranayama is to connect the body and the mind. When you slow down breathing patterns, you can also increase longevity. That is the reason why some animals live longer than humans. The core reason of existence is your breathing pattern. Nadi Shodhana or Alternate Nostril Breathing is one of the most commonly taught Pranayamas. You can make it a part of your life. It involves exhalation and inhalation, through one nostril at a time. When you retain the breath between each exhalation and inhalation, it can lead to conservation of energies. Likewise, you can also practice Anuloma Viloma. It is another variety that can give you the calmness you are looking for, in your life.
Pranayama is the integral part of Yogic Practices also mention in the eight limbs of Patanjali Yoga sutras. Pranayama specifically focus on the increase the efficiency and balancing the breath of an individual. Prana is vital energy of the body and yama refers to the expansion and growth. There are many physiological and psychological benefits by doing pranayama practices daily.
Introduction of Pranayama

Meaning of Pranayama

Definition

Breathing experiment

Conclusion
Advance Kapalbhati Pranayama (Frontal Brain Cleaning Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Kapalabhati Pranayama

Preparation of Kapalabhati for students – Technique One

How to do Kapalabhati Pranayama?
Advance Sheetali Pranayama (Cooling Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Sheetali Pranayama

Preparation of Sheetali for students
Advance Sheetkari Pranayam (Hishing Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions

Duration of practice – Demonstration of Sheetkari Pranayama

Preparation of Sheetkari for students
Advance Bhastrika Pranayam (Bellows Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhastrika Pranayama

Preparation of Bhastrika for students

Technique One

How to do Bhastrika Pranayama?
Advance Bhramri Pranayama (Humming Bee Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhramri Pranayama

Preparation of Bhramri for students

Technique One

How to do Bhramri Pranayama?
Advance Ujjayi (Psychic Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Ujjayi Pranayama

Preparation of Ujjayi for students

Technique One

How to do Ujjayi Pranayama?
Advance Nadishodhana Pranayama (Psychic Network / Chanel Purification)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Duration of practice

Demonstration of Nadishodhana Pranayama

Preparation of Nadishodhana for students

Technique One

How to do Nadishodhana Pranayama?
Advance Kapalbhati Pranayama 2 (Frontal Brain Cleaning Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Kapalabhati Pranayama Two

Preparation of Kapalabhati for students

Technique Two

How to do Kapalabhati Pranayama?
Advance Sheetali Pranayama 2 (Cooling Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Sheetali Pranayama Two

Preparation of Sheetali for students

Technique Two

How to do Sheetali Pranayama?
Advance Sheetkari Pranayam 2 (Hishing Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Sheetkari Pranayama Two

Preparation of Sheetkari for students

Technique Two

How to do Sheetkari Pranayama?
Advance Bhastrika Pranayam (Bellows Breath) 2 & 3

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhastrika Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Bhastrika for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Bhastrika Pranayama?
Advance Bhramri Pranayama 2 & 3 (Humming Bee Breath)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Bhramri Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Bhramri for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Bhramri Pranayama?
Advance Ujjayi (Psychic Breath) 2 & 3

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Ujjayi Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Ujjayi for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Ujjayi Pranayama?
Advance Nadishodhana Pranayama 2 & 3 (Psychic Network / Chanel Purification)

Introduction – Meaning – Benefits – Contradictions – Duration of practice

Demonstration of Nadishodhana Pranayama Two & Three

Preparation of Nadishodhana for students

Techniques Two & Three

How to do Nadishodhana Pranayama?
Satkarma
The Shatkarmas are also called Shatkriyas. It is a set of body purification techniques, with the help of which, you can cleanse your system internally. In order to move ahead in your yogic journey, you need to have a strong body, as it serves as the foundation for yoga sadhana. Shatkarmas consists of six cleansing techniques, like Basti, Nauli, Dhauti, Trataka, Neti, and Kapalbhati. Each of these kriyas target specific organs in the alimentary canal. Apart from just strengthening the body, it also leads to the balance of the Tridoshas. It also helps in the flow of Prana through the Nadis. . Kapalbhati is not only a kriya, but it is also a Pranayama. So, you get to indulge in two practices, rolled into one. It is a forceful breathing practice, that can aid in alleviating stress from your brain. You can also practice Neti, very easily. However, a guide will initiate the process, for you to feel comfortable later on.
Six Steps of Cleansing – Subject focus on Jala Neti & Sutra Neti

Introduction to Six Types of Satkarma

Meaning of Satkarma

Contradictions

Benefits
Introduction to the Practical Jala Neti

Contradictions

Benefits

Preparation of Jala Neti

Demonstration of Jala Neti by Teacher

Technique Practice with students
Introduction to the Practical Sutraneti

Contradictions

Benefits

Preparation

Demonstration of Sutraneti by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students
Introduction to the Practical Kunjala Kriya

Contradictions of Kunjala Kriya

Benefits of Kunjala Kriya

Preparation of Kunjala Kriya

Demonstration of Kunjala Kriya by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Kunjala Kriya
Introduction to the Practical Vat Karma

Contradictions of Vat Karma

Benefits of Vat Karma

Preparation of Vat Karma

Demonstration of Vata Karma by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Vat Karma
Introduction to the Practical Nauli Kriya

Contradictions of Nauli Kriya

Benefits of Nauli Kriya

Preparation of Nauli Kriya

Demonstration of Nauli Kriya by Teacher

Technique Practice with Students for Nauli Kriya
Introduction to the Practical Agneesara

Technique Practice with Students for Agneesara

Demonstration of Agneesara by Teacher

Preparation of Agneesara

Benefits of Agneesara

Contradictions of Agneesara
With presence of teacher
With presence of teacher, students will prepare the class to practice Jala Neti, Sutra Neti, Kunjala kriya, Vat Karma, Nauli kriya and Agneesara them self. Techer will observe the class.
Bandhas

Jalandhara Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Udiyana Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Mula Bandha Advance

Technique Practice with Students

Demonstration

Preparation

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits
Maha Bandha Advance

Introduction

Meaning

Benefits

Contradictions

Duration of Practice

Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Mudra - Gesture
A mudra is a gesture or seal in yoga. You may come across mudras in dance forms as well, however, they are much different. When you practice mudras, you can channelize Prana through the body. There are various kinds of mudras, like Hasta mudras, Kaya mudras, and Chitta Mudras. Hasta mudras are the most important in Yoga practice. According to the Science, Ayurveda, there are five elements or Mahabhutas. Fire, earth, air, water, and ether. Each finger represents one maha bhuta. You can manipulate each element for the betterment of your body and health, and increase or decrease the flow of prana to specific body parts. One of the most commonly used mudras, is Gyan mudra. You can practice it while performing the asanas. It helps in obtaining knowledge and greater wisdom from the universal body. You can practice mudras anywhere, while sitting in your home or workplace, so that is an added benefit of mudras. Get the maximum benefits today.

Jnana Mudra (Psychic Gesture of Knowledge)

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Chin Mudra (Psychic Gesture of Consciousness)

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Bhairava Mudra – Shiva Mudra

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Hridaya Mudra – Heart Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Yoni Mudra – Womb Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Shambhavi Mudra – Eyebrow Center Gazing Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Kaaki Mudra – Crow's Beak Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Ashwini Mudra – Horse Gesture

Introduction

Benefits

Duration Preparation

Demonstration

Technique Practice with Students
Meditation
Meditation is a set of practices that encourage higher states of consciousness, awareness, and focused attention. Moreover, it is not just a part of yoga. Every culture practice meditation. People practice meditation for spiritual as well as religious reasons. In the Western World, meditation has been shown to help people cope with stress, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. It is all about training your awareness. You learn to observe your thoughts and patterns, without any judgement. Moreover, everyone can meditate. There is no age boundation or health boundation. So, it is a universal practice, that goes beyond the physical body. . If you are just starting out and find it extremely difficult to practice meditation, you can also use props, like meditation seats, malas, and singing bowls. It will alleviate the strength of your practice. Meditation can cure the most incurable diseases, as per research. Always practice in a clean and calm place. Lots of sunlight is also important.
Introduction of Meditation/ Meaning and Things

Mantra Chanting with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

Apa Meditation with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

Sixty One Energy Points Discussion

OM Meditation with Meaning and Benefits/Practice

The Practice of Osho Dynamic Meditation

Music Meditation Practice

Dancing Meditation Practice

Walking Meditation Practice

Introduction of Tratak Meditation/Stages/Benefits

The Practice of Dot Meditation

The Practice of Yantra Meditation
Yogic Relaxation Techniques
The answer to life’s stress and tension is yoga. It has been widely researched, that yoga can change your life, by reducing stress and anxiety. No matter, where you are, at work or at home, yoga can help you. If you are new to yoga, you can start your yoga journey with mindfulness. Your breath is the single-most thing, that can alleviate the mind, body and soul. Moreover, mindfulness is the main modality, that can alleviate your symptoms. When you move into the postures, you should ensure to think about your own self-respect and self-care. It is the curiosity towards yourself, that can help you relax. Some of the easy poses, that you must practice today are Sukhasana, Uttanasana, and Tadasana, to name a few. These are very easy for one and all. You can practice the asanas, after a few hours of having your food. When the stomach is full, your body’s energies are aligned toward the stomach. So, you will not be able to utilize them to their full strength. Apart from poses, you can also utilize breathing techniques. Meditation and relaxation are inter-linked. You have to utilize breathing to guide the poses, and it should not be the other way round. That is when, you can gain the true benefits of yoga. The best part of yoga relaxation is that, you can practice it anywhere and everywhere. So, it is universal in nature and beyond boundaries. Start relaxing now, with myriad yoga practices. It is one of the ancient sceiences that has cleared clutter from the minds of millions.

Synopsis of Featured Teachings

Point-to-Point Movement and then Stillness

Point-to-Point Tension and Relaxation

Entire-Body Tension and Relaxation

Point-to-Point Relaxation

Selective Tension and Relaxation of Body Parts

More Detailed Point-to-Point Relaxation with Visualization of Pure White Divine Light at the Cardiac Center

Detailed Point-to-Point Relaxation with Spinal Breathing and “So-Ham”
Alignment, Correction & Adjustment
Alignment and adjustment are fundamental concepts in the practice of Yoga, both for practitioners and instructors. Here’s a breakdown of each:
What is alignment in Yoga?
Alignment refers to the precise positioning of the body in Yoga poses (Asanas) to achieve optimal physical and energetic benefits while minimizing the risk of injury. It involves the correct placement of various body parts, such as the feet, legs, pelvis, spine, arms, and head, in relation to one another and to the ground. Proper alignment ensures that the body is in a balanced and stable position, allowing for the efficient flow of energy (Prana) throughout the body. It also helps to create space within the joints, improve posture, enhance flexibility, and build strength. Alignment principles may vary depending on the specific Yoga style or tradition but generally emphasize alignment with the natural curves of the spine and engagement of relevant muscle groups.

What is Adjustment in Yoga?
Adjustment, also known as hands-on adjustment or assists, involves the gentle physical manipulation of a student’s body by the instructor to help them refine their alignment, deepen their stretch, or experience a pose more fully. Adjustments can provide valuable feedback and support to students, helping them overcome physical limitations, release tension, and access deeper levels of awareness in their practice. Adjustments are typically performed with sensitivity and mindfulness, respecting the individual’s body and boundaries. They may include subtle corrections to alignment, gentle pressure to encourage relaxation or engagement, or supportive touch to guide the student into a safer or more effective expression of a pose.

Roll of alignment and adjustment in Yoga concept

Physical Alignment in Yoga

The Role of Adjustment

Benefits Beyond the Physical

Alignment and Adjustment in Spiritual Practice

The Role of Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga: A Comprehensive Overview

Understanding Alignment in Yoga
Spine
Joints
Muscles
Physical Adjustments
Verbal Adjustments

Components of Alignment

Challenges and Considerations in Adjustment

Integrating Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga Practice

Alignment and Adjustment in Yoga Asanas for Students Homework
Teaching Methodology
TEACHING METHODOLOGY

Teaching is an art and it can be developed through practice and knowledge.

Teach with sincerity and compassion for yourself first and then your students will benefit as well.

Teach from the heart, never from the mind.

Respect that divine energy has honored you to be a teacher to help people.

Changing peoples’ lives into positivity by teaching them yoga and meditation; as a teacher, your inner journey and happiness will grow.

Respect the students, be friendly and professional but at the same time strong inside not to entertain any negativity while teaching yoga.

Surrender to life and divine energy; you will feel guided by the unknown force.

Enjoy teaching mindfully with joy and happiness.

Be present, aware, and energetic all the time during or after the class.

Be regular for your own self-practice of yoga and meditation; you owe it to yourself and your students.

Be aware and sensitive to students’ poses, alignment, breathing pattern, group energy, and allow the teaching and response to happen accordingly and spontaneously.

Pay equal attention to the students but focus more attention on beginners until they catch up with the regular class.

Welcome the students – greeting the students makes them comfortable and feel welcomed.

Start the class on time and end on time. This honors the student since most students have limited time and have sacrificed to get to the class.

Always ask if the students have any physical problems and injuries.

Start the class with some chanting, prayer, or a short meditation.

The voice of the teacher should be audible to everyone and the volume should be according to the group.

Give clear instructions.

Make adjustments verbally and physically.

Appreciate and motivate the students during the class.

Move around the class effectively to see all the students and to check their alignment.
Yoga Philosophy
Along with the practical applications of yoga, you need to fall back at times, on the foundation of yoga. That is what Yoga Philosophy is all about. The main philosophy of yoga states that the minds, body, and soul are all one. You need to know about the philosophical ideas, to be able to utilize the various practices under the umbrella of yoga. In yoga, you cannot choose one or leave out another aspect. The entire practice has to be carried out in totality. Spiritual ignorance can only create suffering, and mothing more than that. So, you need to amass the wealth of knowledge that philosophy of yoga offers. You can call it the blue print of your yogic practice. It enlists what all you should follow, and what you should not. The main principle of yoga is that the mind, body and soul is one. You cannot separate one from the other. It also allows the concept of God. It is amongst the six orthodox schools.


Yoga Sutra – discipline, types of thoughts, God

7 Chakras – Muladhara, Swadhisthana, Manipur, Anahata, Visudha, Anjya, Sahasrara

Three types of gunas – Satva, Rajas & Tamas

Three types of body – Sthula, Sukhma & Karana

Types of Yoga (Hatha, Karma, Bhakti, Astanga)

What is yoga? Introduction of Yoga

What is philosophy?

What are the obstacles to yoga?

What are the causes of pain?

What are the eight limbs of Yoga?

Exercises

Exam
Mantra Chanting
Mantras are group of syllables, or complete words, or phrases. Most religious and spiritual practitioners, believe them to have originated from Sanskrit. Om is the believed to be the first sound that originated on earth, and has divine connotations. It produces higher vibrations in the body and mind. Mantras also serve an important role in Tantra. You can also term it as a mind vibration that helps to focus the thoughts and feelings, and the highest intention. With time, the mantras and their vibrations sink deeper into the consciousness. You can practice mantra recitation to make your energies vibrate at a higher level. Om is one of the mantras sounds that assumes a lot of significance. It releases subtle energies, that can aid your meditation and yoga practice. You can chant mantras at any time, and place. But they have the maximum significance, when you chant them at the Brahma Muhurta. You will feel the vibrations emanating from the mantras, as you make them a part of your life.

What is Mantra?
The word “mantra” is derived from two words. The first word is “Manas” or “mind,” which relates to the “man” syllable means “To think”, the second word is a suffix “Tra” which means instruments, tools, protect, or free from. Therefore, the word Mantra in its most literal sense means “to free from the mind Mantra is a tool used by the Mind to be free from all kinds of distractions of the Mind field.
Benefits of Mantra Chanting

Hatha Yoga Mantra: Yogena Schitasya Padena Vacham

Health Mantra: Trayambakm Yajamahe

Gayatri Mantra: Om Bhur Bhubah Swaha

Ganesh Mantra: Om Vakratunda mahaakaaya

Morning Mantra: Karagre Vasate Laxmi

Guru Mantra: Akhanda Mandalakaram Guru Brahma Guru Visnu

Aum Mantra: Aum...Aum...Aum

Shanti Mantra: Om Sarve Bhavantu Sukhinah Om Saha Na bhavatu, Saha Nau Bhunaktu Om Asato Maa Sad-Gamaya, Tamaso Maa Om Purna madah Purna midam

Astanga Vinyas Mantra: Vande Gurunam Charanara Vinde Avahu Purusa Karam, shankh

Astanga Vinyas Closing Mantra: Swasti prajaabhyah paripala

Purna Mantra: Om Purna madah Purna midam
Bhajan or Spiritual Songs
A Bhajan is basically a devotional song, that you sing to glorify any particular deity or the lord in general. It is usually the ancient scriptures, from where it originates. You can sing it straightforward, or recite it like a mantra, or add some melody. Bhajan is related to Bhakti. You will learn of different styles of Bhakti songs from different parts of India. You may hear them coming from various Hindi complicated dialects, and some using various day-to-day occurrence in in simple words and forms. You will be able to get rid of mental issues, once you make such devotional hymns a part of your practice. . This kind of devotional singing is very popular at Indian pujas and rituals. Slowly the wet is also opening up to its possibilities, as it tends to calm the mind. It is a spiritual practice of sorts, where everyone participates in one go. You can also start doing this practice alone, from home.


Shiva Shiva Shambhu, Shiva Shiva Shambhu, Mahadeva Shambhu, Mahadeva Shambhu, Shiva Shiva Shambhu.

Govinda Govinda Govinda Bhaja Gopala, Gopala Gopala Gopala Bhaja Gopala.

Govinda Bol Hari Gopal Bol, Radha Ramana Hari Govinda Bol.

Hare Krishna Hare Krishna, Krishna Krishna Hare Hare, Hare Rama Hare Rama, Rama Rama Hare Hare.

Sita Ram Sita Ram, Sita Ram Jai Sita Ram, Radhe Shyam Radhe Shyam, Radhe Shyam Jai Radhe Shyam.

Raghupati Raghava Rajaram, Patita Pavana Sitaram, Ishwar Allah Tero Nam, Sab Ko Sanmati De Bhagavan.

Natavara Nagara Nanda Bhajore Mana Govinda, Natavara Nagara Nanda ... Karo Nama Roj Prema se, Mana Ko Dho-Nitya Niyama se, Nirmala Mana Prabhu Ko Pasanda Hei, Mat Karo Mano Ko Ganda, Bhajore Mana Govinda.

Jai Jai Radha Ramana Hari Bol, Jai Jai Radha Ramana Hari Bol.

Ganga Aarti
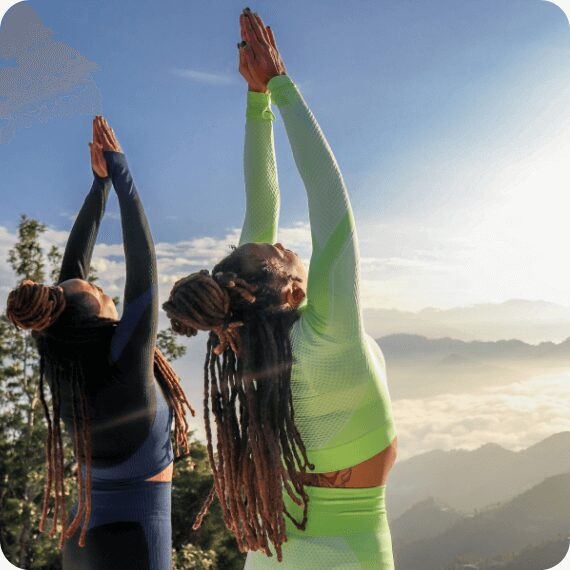

Himalayan Excursion
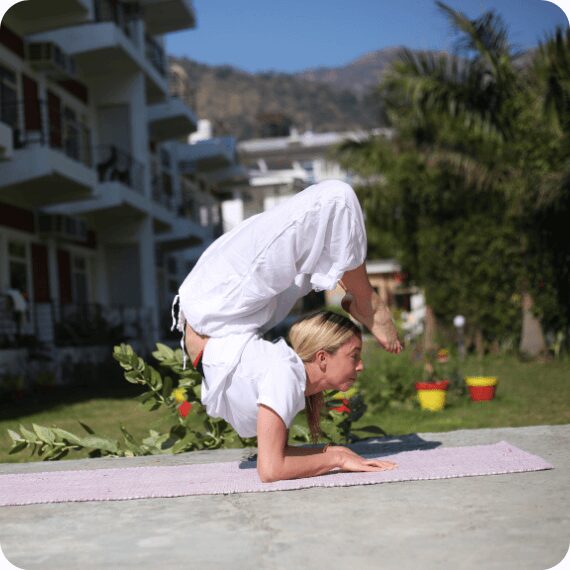

Hatha Yoga Workshop
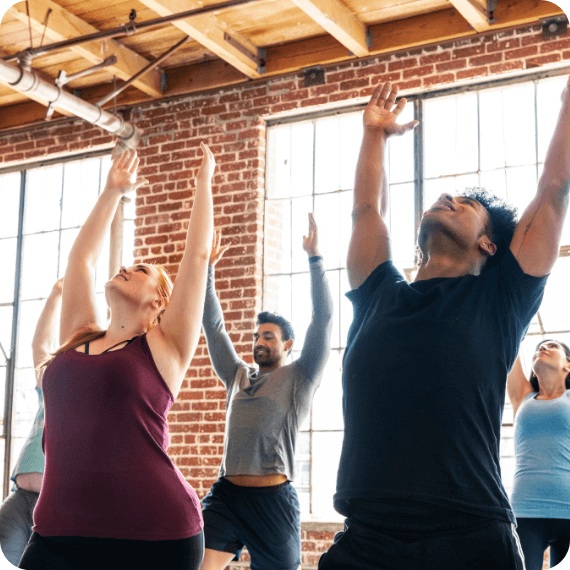

Hypertension Class

Ayurveda Class

Prenetal Yoga Class

Cushion

Zen Bench

Yoga Chairs

Yoga Belt

Bolsters

Yoga Mats

Japa Mala
Neti Pot

Notebook & Pen

Yoga Books

School Handbag

Yoga Pant
T-Shirt
Our retreat center offers comfortable and serene accommodations to ensure a peaceful and rejuvenating experience. We provide a variety of options to suit your needs and preferences.

27 Days Accommodation
2nd - 28th of each month

9 hours daily classes

Small Size Batch 15 Max

Yoga Alliance Certificate

Study Materials

Fire Ceremony

Free Yoga Equipment

3 Daily Nutritious Meals

Yoga Kitbag

Classes at Ganga Beach

Naturally ventilated, soothing spaces

Private Washroom

Cultural Program

Free WiFi

HImalayan Excursion

Ganga Arti
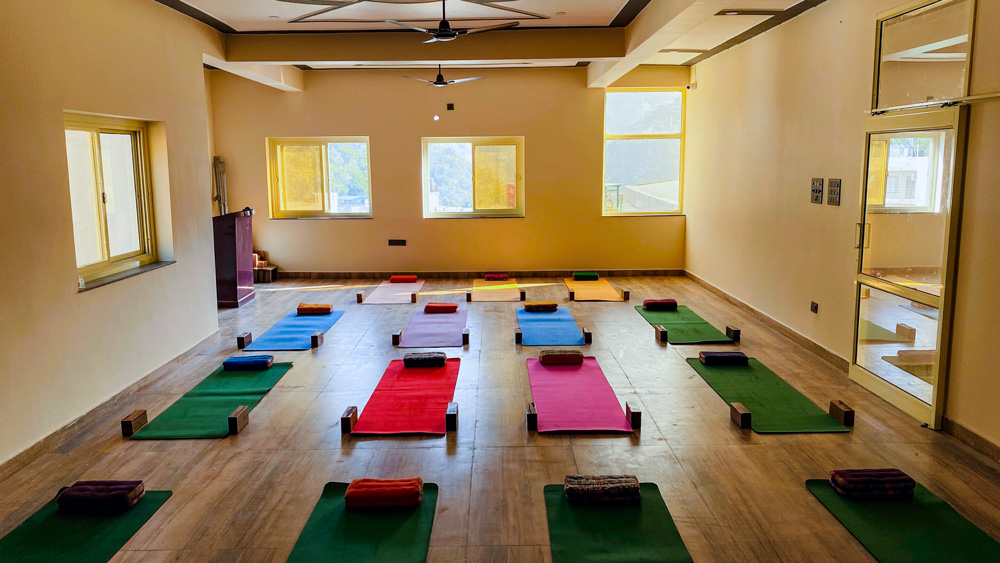



Rated 4.9 Stars by 3000+ Students
Dates
Private
Double sharing
Seats left
Book your spot
The 300-hour students who have not yet received their 200-hour certification from Hari Om Yoga Vidya School will be merged into the 200-hour classes, based on their individual needs and eligibility.
Dates
Private
Double sharing
Book your spot
Rated 4.9 Stars by 3000+ Students
Posted on

Experience Real-Time Learning from the Heart of Rishikesh
Experience Real-Time Learning from the Heart of Rishikesh
Ready to Transform Your Life?
Take the first step towards a healthier, happier you.
Advance Your Practice & Deepen Your Teaching Skills
The 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh is an advanced-level certification program designed for dedicated yoga practitioners who have completed their 200-hour training and aspire to refine their skills. Hosted in the serene surroundings of Rishikesh—the Yoga Capital of the World—this course offers an in-depth study of traditional yoga styles, advanced asanas, yogic philosophy, and meditation techniques.
Our 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training Course in Rishikesh is a Yoga Alliance-certified program, providing international accreditation for those who wish to teach yoga globally. Whether you're looking to elevate your personal practice or take your teaching career to the next level, this course will provide you with the expertise, confidence, and spiritual depth needed to succeed.
Why Choose Our 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh?
Who Can Join This 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training Course in Rishikesh?
This 300hr Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh is ideal for:
✅ 200-hour certified yoga teachers looking to advance their knowledge and teaching methodology.
✅ Yoga practitioners who want to gain a deeper understanding of yogic philosophy, anatomy, and alignment.
✅ Individuals passionate about Kundalini Yoga, meditation, and spiritual awakening.
Course Highlights of the Best 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh
1. Advanced Asana & Alignment
2. Kundalini Yoga & Energy Activation
3. Pranayama, Meditation & Mantra Chanting
4. Yogic Philosophy & Ethics
5. Teaching Methodology & Hands-on Practice
6. Ayurveda & Yogic Lifestyle
Why Rishikesh for Your 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training Course?
Rishikesh is renowned for its spiritual energy, ancient ashrams, and deep yogic traditions. Training here offers:
🌿 A Pure Yogic Atmosphere – Meditate by the sacred Ganges River and practice yoga in serene Himalayan surroundings.
🧘 Learning from the Best – Train under experienced yoga masters with years of expertise.
🏡 A Transformative Experience – Immerse yourself in authentic ashram life, connecting with like-minded yogis.
Certification & Career Opportunities
Upon successful completion of our 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh, India, you will receive a Yoga Alliance-accredited certification, allowing you to:
✔ Teach yoga globally with an advanced qualification.
✔ Deepen your personal practice and knowledge.
✔ Conduct workshops, retreats, and specialized training programs.
Enroll in the Best 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training Course in Rishikesh Today!
Are you ready to elevate your yoga journey? Join our best 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training Rishikesh program and experience a life-changing transformation.
📍 Location: Rishikesh, India
📅 Upcoming Batches: [Check Dates]
💰 Course Fee: $1650
🎟 Limited Seats Available!
👉 Apply Now & Begin Your Advanced Yoga Journey!
Experience the serenity & transformation of yoga.
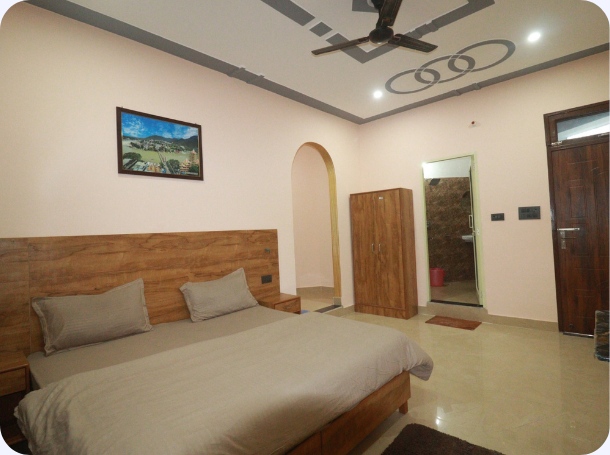
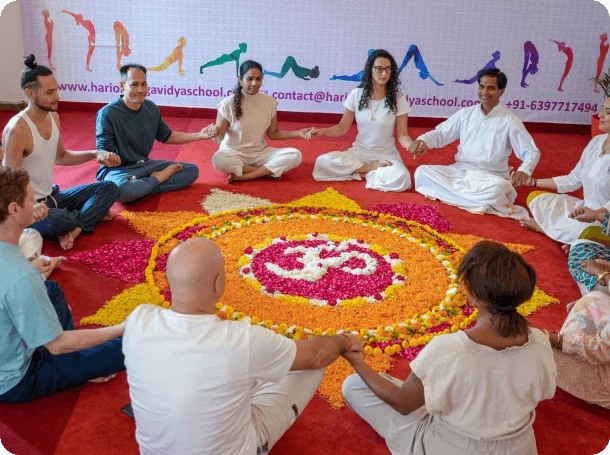
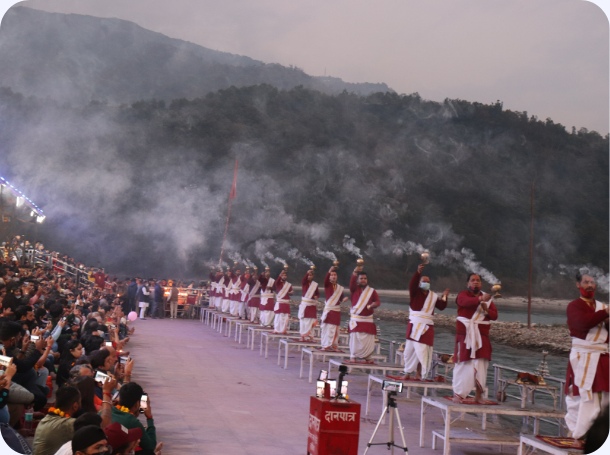
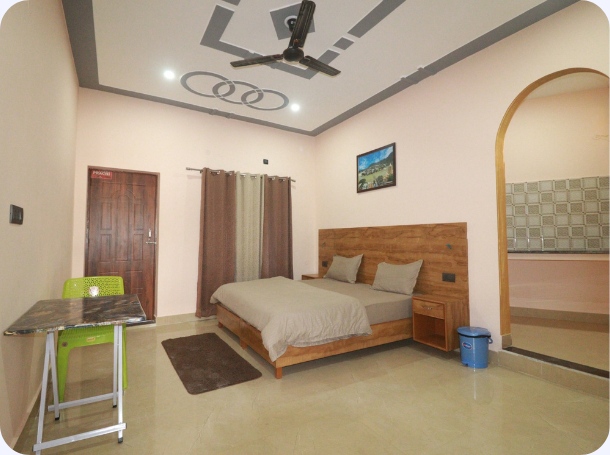
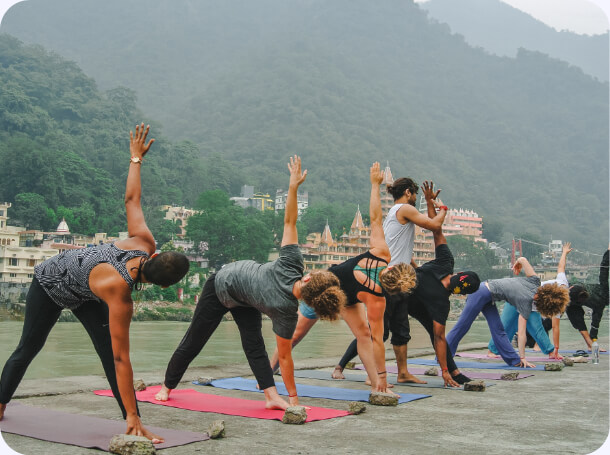
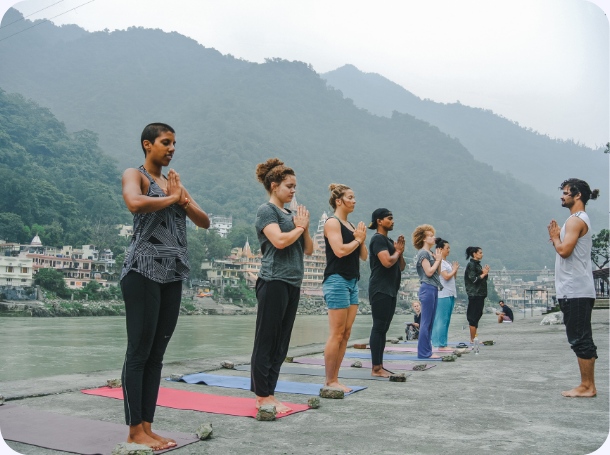
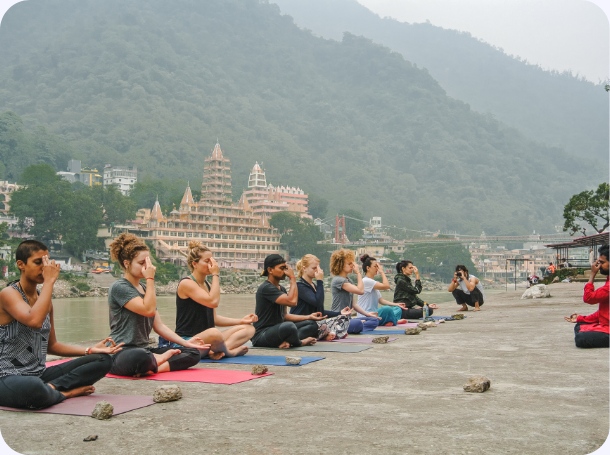
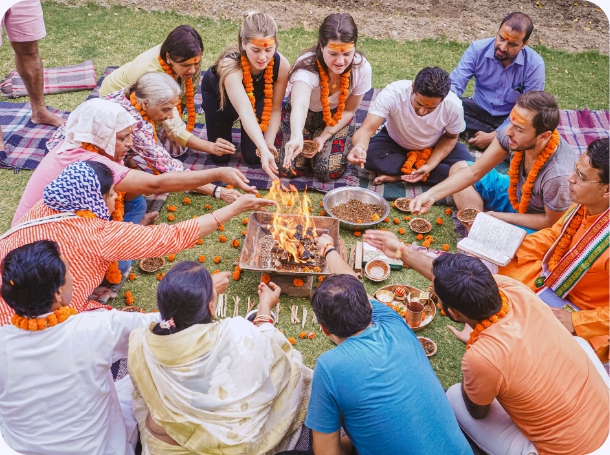
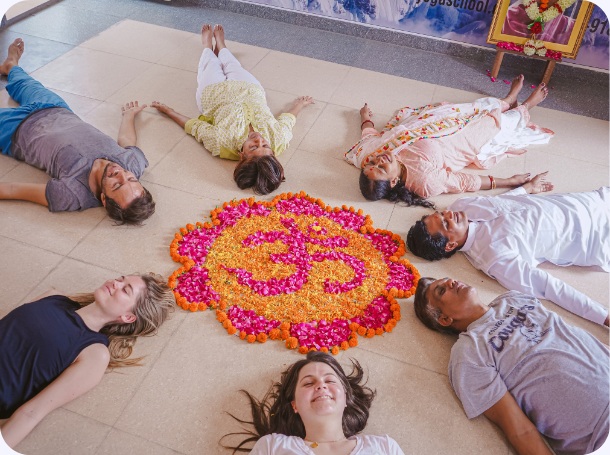
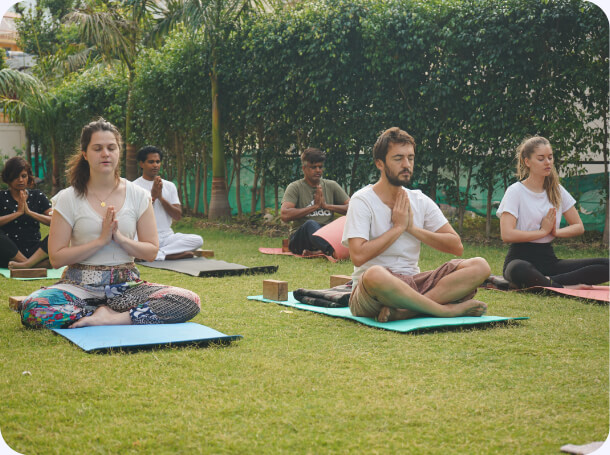
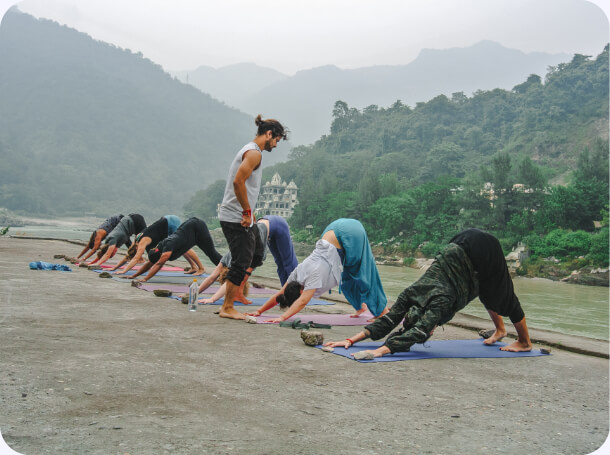
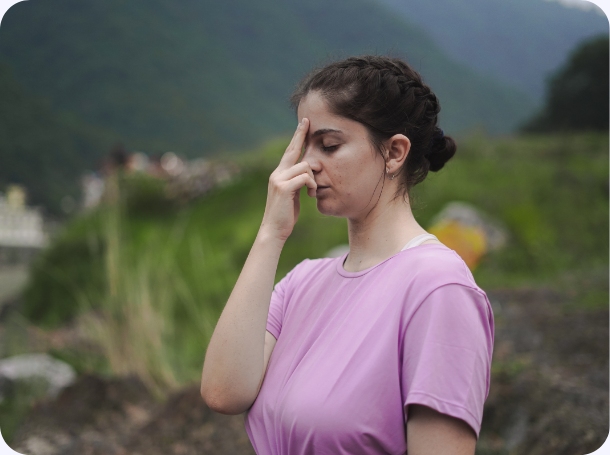
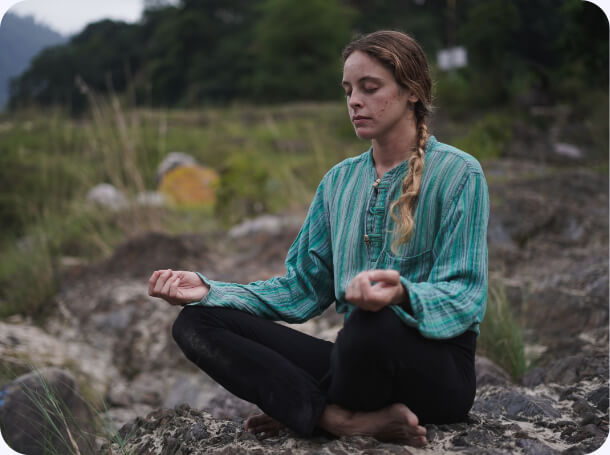



















Watch Our Stories Unfold
Inspiring Stories from Our Students
Frequently Asked Questions
Get all your questions answered here
Our 300 Hour Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh is designed for students who have already completed a 200-hour yoga teacher training from a Yoga Alliance-certified school. If you’re looking to deepen your practice, expand your teaching skills, or specialize in Kundalini Yoga, this course is perfect for you.
The course includes Hatha Yoga, Ashtanga Vinyasa, and Kundalini Yoga, along with advanced practices in Pranayama, Meditation, and Yoga Philosophy. Special emphasis is placed on Kundalini awakening techniques, energy channeling, and deep meditation.
Yes! Our 300hr Yoga Teacher Training in Rishikesh is Yoga Alliance-certified, which means you’ll receive a globally recognized certification that qualifies you to teach yoga anywhere in the world.
The daily routine is immersive and structured to help you grow physically, mentally, and spiritually. It includes:
The schedule ensures a holistic yogic experience in Rishikesh, allowing you to immerse yourself fully.
Rishikesh is known as the Yoga Capital of the World, offering an authentic yogic environment unlike any other. Practicing yoga near the sacred Ganges River, surrounded by the Himalayas, enhances spiritual growth and deepens your understanding of yoga. It’s the ideal place for advanced yoga teacher training.
No prior teaching experience is required, but you must have completed a 200-hour training. This course helps you master advanced teaching techniques, sequencing, and alignment, giving you the confidence to teach yoga professionally.
We provide comfortable accommodation in a peaceful, ashram-style setting. The rooms are clean, well-ventilated, and ideal for deep practice. You’ll also enjoy healthy, sattvic vegetarian meals prepared according to yogic and Ayurvedic principles, supporting your physical and mental well-being.
You can apply online through our website. Early registration is recommended, as spots fill up quickly. Click [here] to check upcoming batch dates and secure your seat for a life-transforming yoga experience in Rishikesh.
About
Teacher trainings
Yoga retreats
Quick Links

Copyright © 2009-2025 Hari Om Yoga Vidya School ®
Feel free to contact us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. We are available 24/7.